Quick SRG50 Configuration
The Survivable Remote Gateway 50 (SRG50) is a new
member of the Nortel family of survivable IP telephony branch office solutions that offer
business continuity and public switched telephone network (PSTN) failover for voice over
IP (VoIP) networks.
The Survivable Remote Gateway 50 (SRG50) operates as follows:
- In Normal mode the main office will provide the branch office with outgoing PTT
trunking, and route any local incoming DID trunks to the appropriate desk, via IP
trunking. The branch office IP sets will auto forward and register with the main office.
- In Survivable mode (ie, the WAN is down) local PTT trunks will be used outgoing calls,
incoming DID is routed locally. The branch office IP sets register with the SGR50.
- When the LAN is restored, branch office IP sets will automatically re-register with the
main office, and normal mode is resumed.
The SRG50 supports up to 32 survivable IP users.
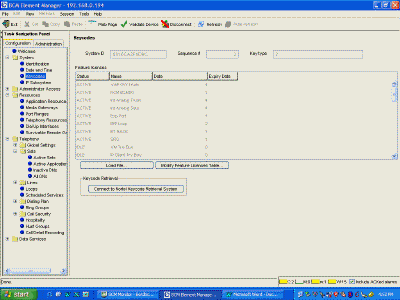
| To make a BCM50 into an SRG50, just enter the required keycodes! SRG
mode needs a keycode, and you may need others for IP trunking, expansion modules, etc..
Sometimes manually entering a KeyCode can be problematic, but using the keycode file
(Load File), stored on a USB drive, seems to work everytime! |
 |
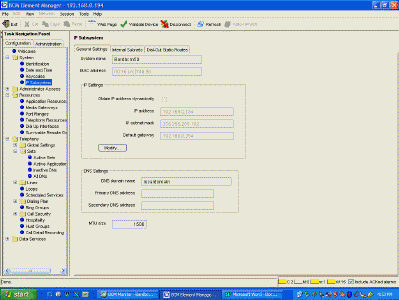
| Edit the SRG50 IP address as required - the default gateway is the
Private IP address - eg, Nortel Contivity 600, LAN 0 address. Also, configure the
type of dialing plan (CDP or UDP).
Configuration > Telephony > Dialing Plan > Private Network > Dialing Plan -
Private Network panel > Private Network Settings subpanel
Enable MCDN TAT.
Configuration > Telephony > Dialing Plan > Private Network > Dialing Plan -
Private Network panel > Private Network Settings subpanel |
 |
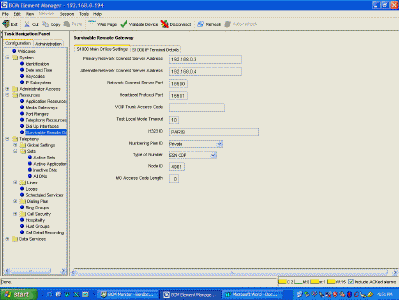
| Edit Resources>Survivable Remote Gateway (this menu item is only there
if the keycode is entered). Enter the Main Office CS1000 IP addresses.
We use ESN CDP numbering. |
 |
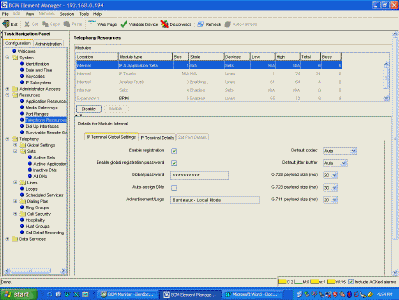
| Edit Resources>Telephony Resources Advertisement logo is whats
displayed on the phone in "Local Mode", make sure the payload settings are correct. |
 |
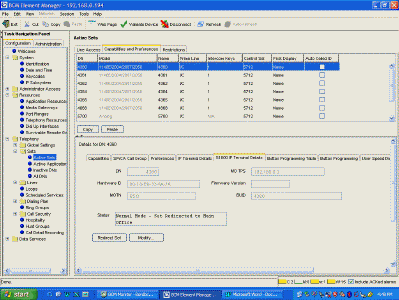
| Add the I2004 phones, they register WITH THE SRG (port 7300) - if the
Main Office settings are correct, they will automatically be redirected by the SRG to the
Main Office. Status: Normal Mode means everything is correct, the set is redirected
(under SRG control) to the Main Office |
 |
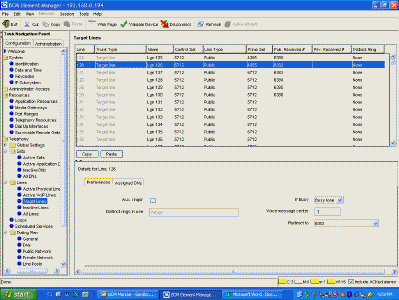
| ROUTING Destination codes and routes must be defined to route calls in
and out of the SRG50. This process is not automatic, it must be defined! These paths are
VIRTUAL - so don't worry about tromboning.
Local (SRG) DID Trunks must be routed to the Main Office with destination codes and
routes. The NRS will send the call back to the SRG to be answered.
Here, Target Line 126 receives digits 6382. It is forwarded to 8082, which is a destination code. |
 |
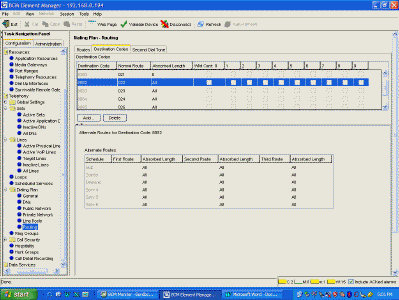
| Destination Code 8082 will use Route 22, and delete all digits (the 8082) (digits
are deleted in the destination code, but may be added in the route)
NOTE: To allow tandem
dialing from the main office through the SRG , or to redirect SRG IP telephones to use the
SRG local PSTN, you must specify a remote package that provides access to the PSTN line
pool. This remote package is then assigned to each VoIP trunk.
Configuration > Telephony > Call Security > Remote Access Packages |
 |
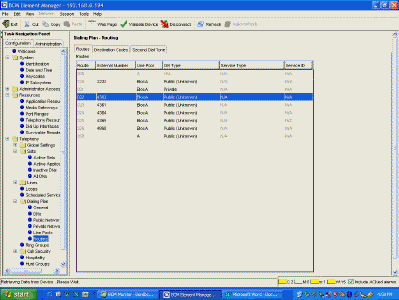
| Route 22 will use the VoIP trunk route (BlocA) and insert digits 4362 NRS
(at the Main Office) will route this call to extension 4262, which just happens to live on
our local SRG.
The result is - an incoming Target Line receiving 6382 will ring on extension 4362.
'9' is also defined as a destination code, but in Normal Mode dial-9
calls are handled by the Main Office. However, in Local Mode (ie, the WAN is down and the
Main Office is unreachable) this destination code allows calls out of the SRG using, in
this case, POOL A - which is our local PTT trunk pool. |
 |







