SSH to a CS1K (Mac)
Windows users can connect with PuTTY. With macOS, SSH is built in, no additional software is necessary.
The Call Server will obviously need to be connected to a network, have some PTY's (pseudo TTY's) built, and you'll need to know it's IP address. The first two are probably a given, the third easy to find. Make sure there are 3 PTY's, if not, add them in case one locks up.
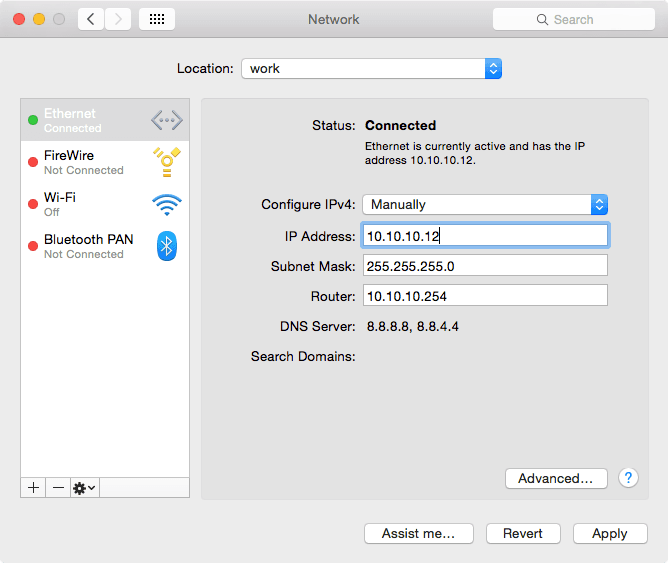
IP Address:
In the Network Preference Panel, click the network interface, select 'Configure IPv4 Manually', enter an appropriate IP address / subnet mask / router (gateway), and connect to the ELAN data switch.
Terminal:
Open Terminal (Applications/Utilities/Terminal.app), and PING the Call Server. Type Ctrl-c to exit ping.
$ ping 10.10.10.5 PING 10.10.10.5 (10.10.10.5): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.10.10.5: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=0.245 ms 64 bytes from 10.10.10.5: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.273 ms ^C
If the ping is successful, enter SSH admin2@host to open a session with the Call Server.
Log into the Call server console using the standard LOGI command, ADMIN2/0000.
Enter LOGO to close the session. To close the connection, enter ~. (tilde, period).
$ ssh admin2@10.10.10.5 The authenticity of host '10.10.10.5 (10.10.10.5)' can't be established. DSA key fingerprint is SHA256:mKn33bl3Txp7ZyPQVat5fmOkRh8lXT39X6F8PErb0sg. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '10.10.10.5' (DSA) to the list of known hosts. User Authtication admin2, welcome to Nortel CS1K Call Server Password: <password> Login Success. SEC0029 SECURITY WARNING: THIS SYSTEM CONTAINS INSECURE PASSWORDS, NOTIFY YOUR SYSTEM ADMINISTRATOR . TTY #13 LOGGED IN admin2 12:31 30/4/2016 >
Connection Issues:
Sierra (macOS 10.12) uses OpenSSH v7.2 (El Capitan used OpenSSH v6.9) which no longer supports some of the older, less secure algorithms by default. If an SSH connection is refused with one of the following errors, the fix is to re-enable them in ssh_config.
Enter the command: sudo nano /etc/ssh/ssh_config and add the following two lines to the end of the file:
HostkeyAlgorithms +ssh-dss KexAlgorithms +diffie-hellman-group1-sha1
A 'better' solution is to create ~/.ssh/config with those two lines, or better yet, applied more specifically:
# settings for all hosts HostkeyAlgorithms +ssh-dss # host specific settings Host cs1k HostName 10.10.10.5 ← for this host... KexAlgorithms +diffie-hellman-group1-sha1 ← use this algorithm User admin2
This example only allows 'diffie-hellman-group1-sha1' for a specific host, and sets a default username - connect with ssh cs1k
The 'diffie-hellman-group1-sha1' algorithm is used on most Cisco routers, firewalls and switches, so may be added to 'all hosts'.
• If an SSH connection is refused with the following error, the fix is to update the offending fingerprint.
Enter the command: ssh-keygen -R <host> to clear the old fingerprint, and then try connecting again.
Alternatively, remove the specific host entry fingerprint in ~/.ssh/known_hosts (or remove the file).
Note: on Unix-based systems like OS X, the tilde character (~) references the user's home directory.
If you use SSH more than casually, install Shuttle for a quick and simple menu-bar SSH shortcut.
References:
- PING is one of the oldest and most useful UNIX commands, it was written by Mike Muuss in 1983 at the US Army Defense Ballistics Lab.
Muuss sadly lost his life in a car accident on I95 in Maryland on November 20, 2000 (age 42). - SSH (Secure Shell) was originally developed by Tatu Ylonen in 1995 in response to a hacking incident in the Finnish university network.