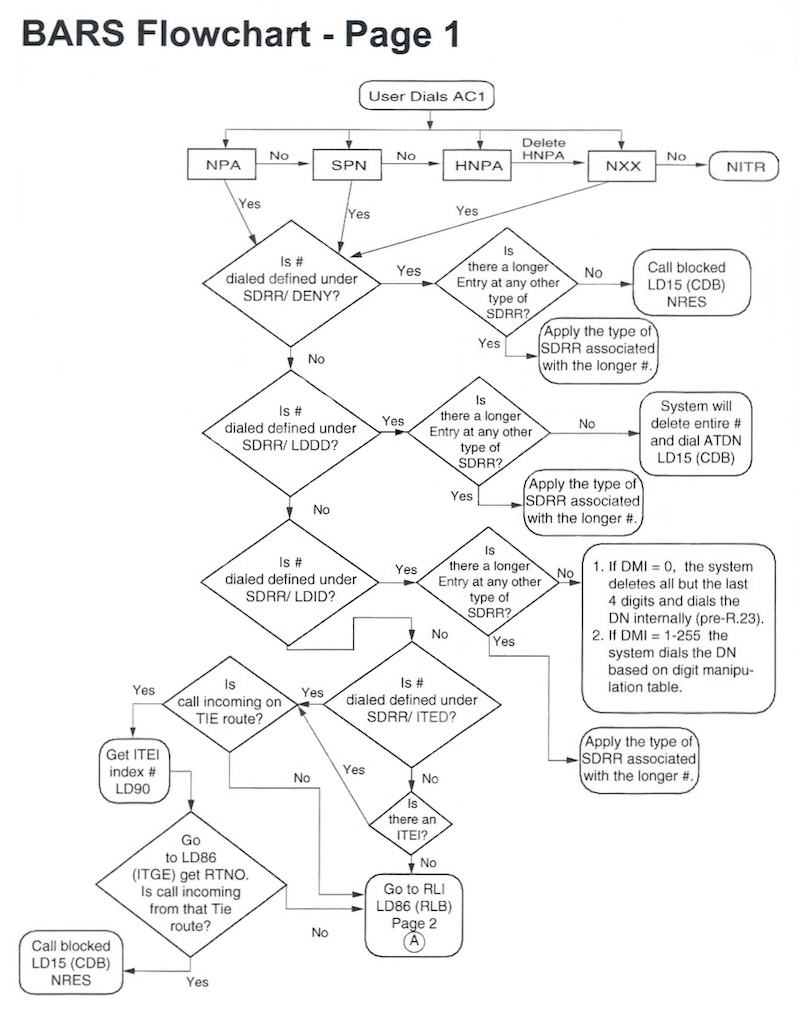
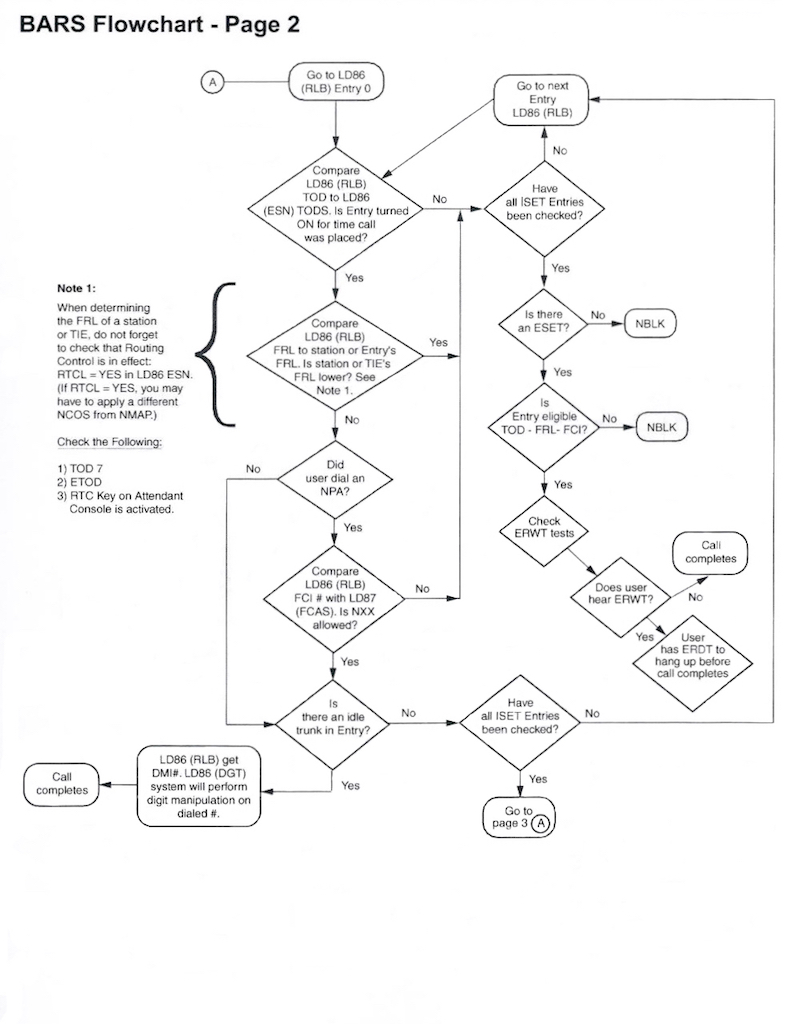
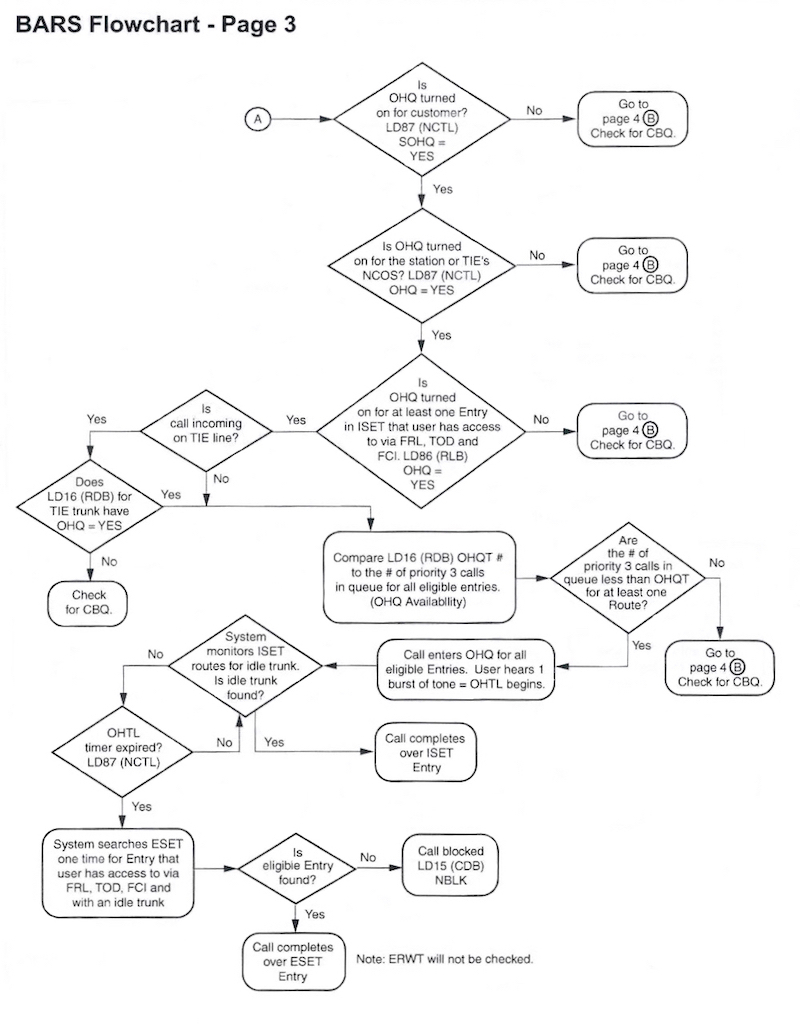
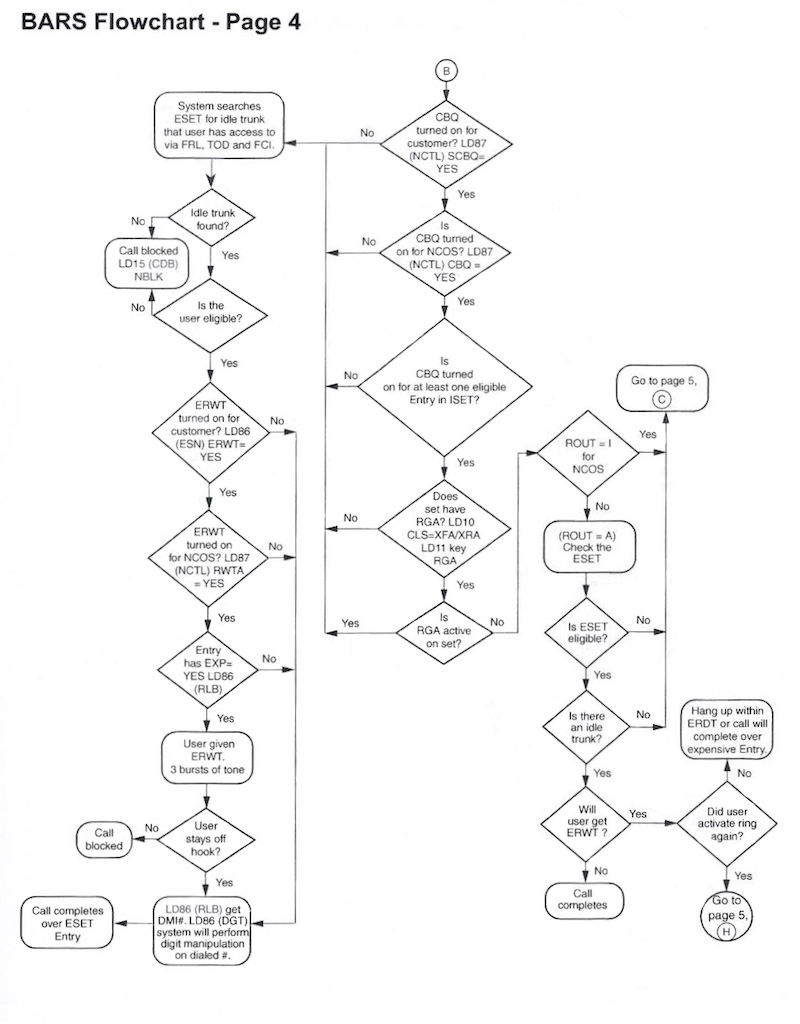
BARS Flowchart
Basic Alternate Route Selection is used to prevent users from placing unauthorized toll calls, and to route outgoing calls over the most appropriate and/or least expensive facility available at the time the call is placed. BARS is triggered by dialing an access code (AC1), followed by a subscriber number.
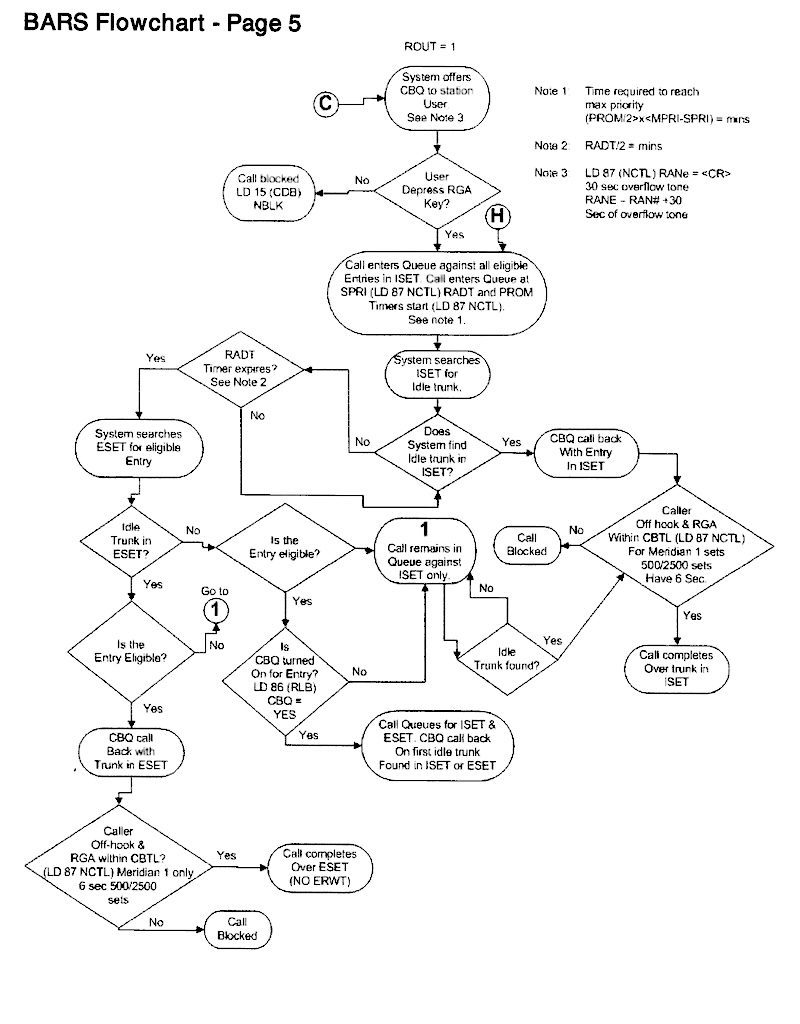
The following BARS Flowchart shows what happens after AC1 is dialed. There are lots of twists and turns on this journey!
Process:
A user dials the BARS access code, AC1 (9), followed by a number:
- BARS tries to match (a portion of) the dialed digits in the tables
- If a match is found, a route is determined for the call
- FRL (NCOS) is checked (and optionally TGAR)
- Digit manipulation is applied (if necessary)
- If a trunk is available, the digit string is sent.
If any of the above steps fail, the caller hears re-order (fast-busy).
A Network Interdigit Timer (NIT) determines end-of-dialing, NIT is set in LD 15, TIM_DATA.
Dial a # (octothorpe, pound, number sign) to bypass NIT and analyze the dialed digit string.
The overlays:
- LD 86 - FEAT: ESN
- Define AC1 / AC2 codes
- Enable CDP for customer
- Second dial-tone (DLTN)
- Expensive Route Warning Tone (ERWT)
- Check TGAR on BARS calls (default: No)
- LD 87 - FEAT: NTCL
- Define NCOS to FRL maps (1 to 1)
- Define RWTA (expensive tone) for a NCOS
- LD 90 - FEAT: NET
- Type = NPA (Number Plan area code)
- Type = NXX (Central Office Code Translation)
- Type = SPN (Special Number Translation)
- LD 86 - FEAT: RLB
- Define Route List (RLI) entries (ENTR #)
- LD 86 - FEAT: DGT
- Digit Manipulation tables (applied to RLI)
- More about the SPN Data Block and SPN Alternate Routing.
- Information about Cellular Gateway Routing and Alternate Long Distance Carriers.
- Refer to the BARS programming course for a more details.
- Record RLI's with the Route List Index Worksheet